Due to its varied climatic and ecological zones, Kenya provides a suitable environment for growing vegetables for export. The country has a well-qualified and experienced agricultural labor force, and its location and well-developed connectivity with key markets are key elements in the growth of fresh produce exports.
Kenyan vegetable growers are organized into either large group farms, single farms, or out-growers who produce for export companies under contract. The latter has to follow rules put in place by the contracting company. This is to ensure that homogeneity and food safety standards are met to the satisfaction of the product’s end-user.
All Kenyan produce for export is produced under strict adherence to Global GAP stipulations, which dictate the requirements being met before anyone is allowed to export vegetables. Sufficient measures are put in place to ensure that sanitary and phytosanitary basics are considered by all growers.
Several government institutions are tasked with the certification and inspection of the Kenyan produce, which has led to steady growth in both export value and volume.
Economic importance of Export Vegetables in Kenya
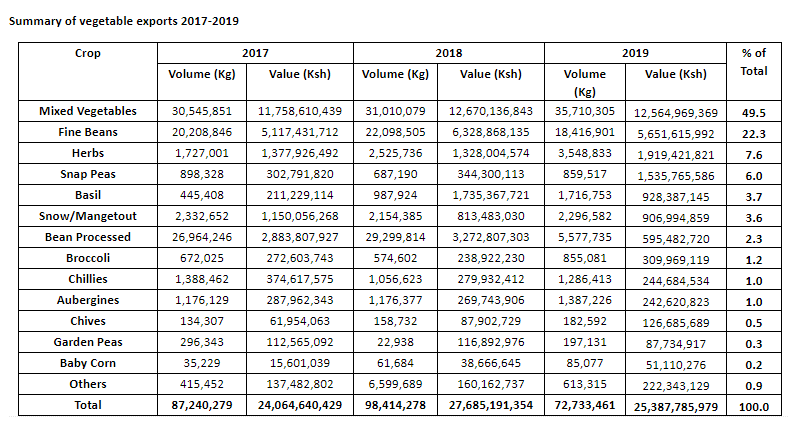
Kenya is one of the key exporters of fresh vegetables to the European Union with over 87,000 tons per year. These exports are valued at more than 24 billion Kenya shillings.
Besides earning the country revenue through exports the vegetable segment contributes enormously to job creation for Kenyans and expatriates working in the industry. Thousands of Kenyans earn a living either directly or indirectly by working in or with the vegetable-growing farms.
Farms employ many in areas like growing, transport, administration, procurement, security, etc. Others, while not directly employed by the vegetable growers, earn through the providence of farm inputs like seeds, farm infrastructure (greenhouses, shade nets, irrigation systems) pesticides, fertilizers, and packaging materials. Others still, earn their living via providence of such services like training, logistics communication, etc. These are rendered to the vegetable growers.
The majority of all these people are tax payers, benefitting the government as they benefit themselves.
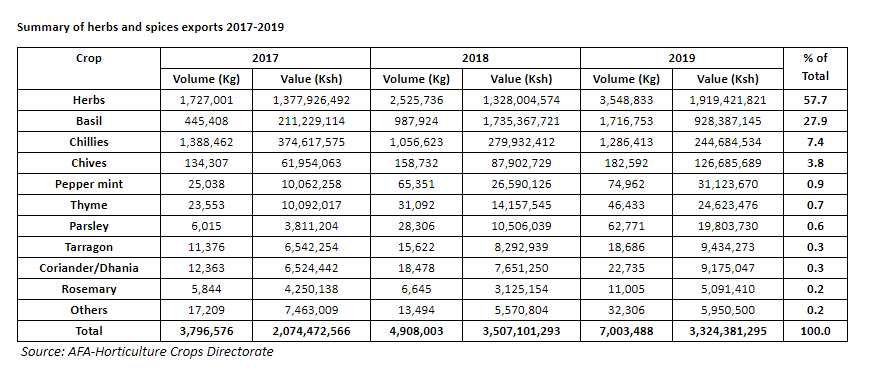
Herbs and Spices
A health-conscious middle class is driving the growth of culinary herbs and spices in the international markets, which has seen a meteoric rise and currently stands at $2.3 billion according to data from the International Trade Centre. Key markets include the EU, which in 2013 imported 302,000 tonnes of spices and herbs from developing countries like Kenya worth € 1 billion.
The spices and herbs with global demand include the following: Pepper, Parsley, Paprika, Marjoram, Capsicum (chillies and cayenne pepper) Oregano, Pimento (allspice), Thyme, Coriander, Bay leaves, Cinnamon, Rosemary, Ginger, Basil, Nutmeg, Mint, Caraway, Savoury, Turmeric, Dill, Cumin, Tarragon, Cloves, Sage, Mace, Cardamom, Anise, Fenugreek, Saffron, Vanilla, Fennel seeds and Juniper berries.
According to AFA, the herbs and spices that are being promoted for exports include the following:
- Herbs (Chives, Rosemary, Dill, Marjoram, Basil, Mint, Parsley, Coriander, Curry leaves & Celery).
- Spices and Chillies (thin, long, bullet & birds’ eye).
The European Union (EU) market is the second-largest market for seasonings, spices, and herbs in the world, accounting for about Euros 1.2 billion. According to the ‘Centre for Promotion of Imports from Developing countries (CBI), the EU imports 97% of its herbs and spices from developing countries. European imports of spices and herbs from developing countries have grown significantly in recent years, by 6.1% annually from 257,000 tonnes in 2012 to 426,000 tonnes in 2019. Therefore, the EU constitutes a critical market to focus in the development and promotion of herbs and spices for exports.
Equally important is the global market, which CBI projects to have a growth of 5.1% between 2017 and 2021.
WHY CHOOSE US
Sales
employed directly
Impacted
Annually
Some of the vegetables grown in Kenya
Kenya grows numerous types and varieties of vegetables. The main focus is on snow peas, garden peas, French beans, and broccoli.